Speed test FAQs
Understanding your speed test results
You did a speed test, so what's next? We'll look at what those results tell you about your internet performance. Check out the top questions about speed test results. Scroll down to find more answers about all your speed-related questions.
Top speed test questions
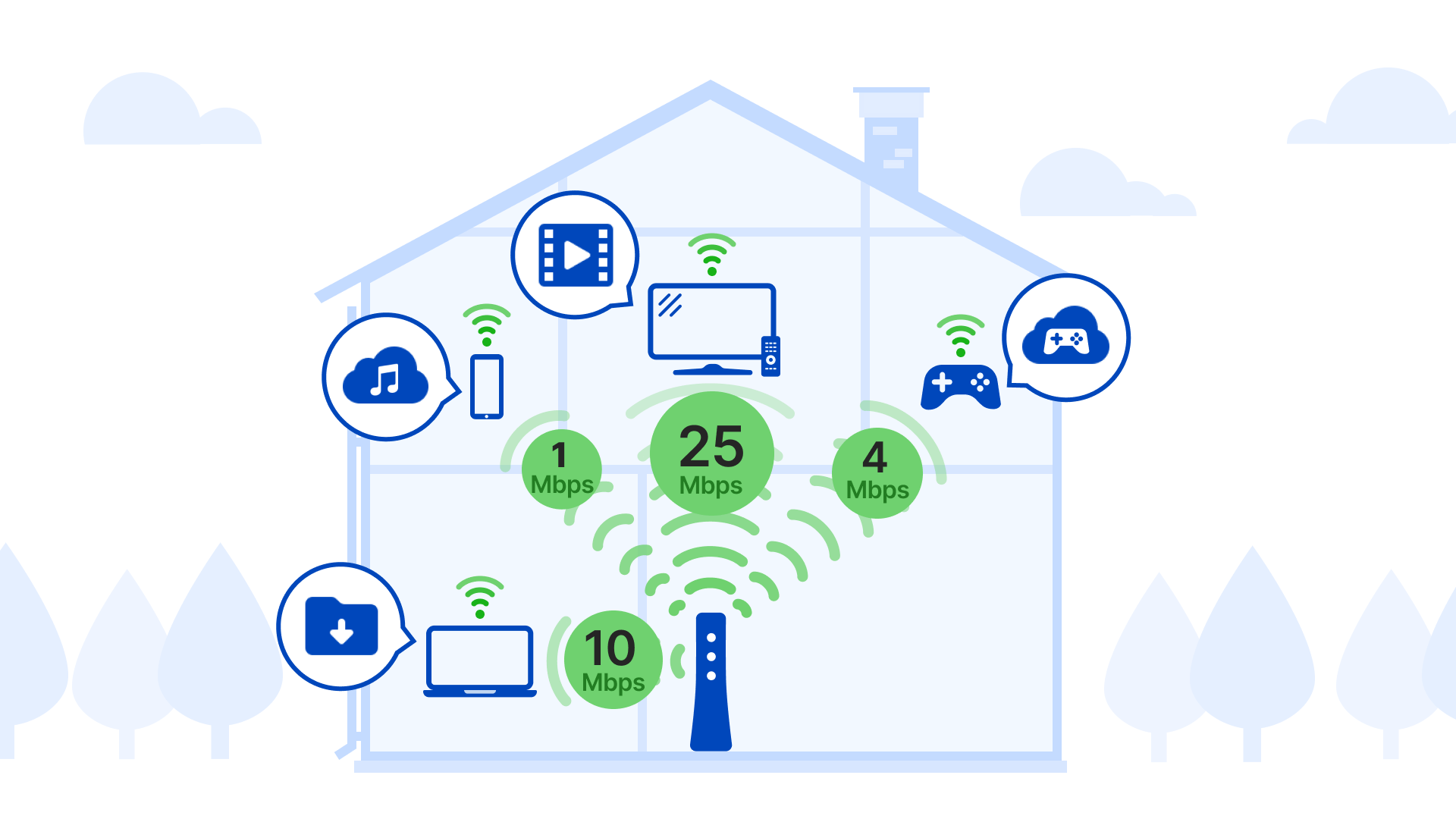
Below are recommended speeds for common activities. Learn more about what internet speed you need for different activities.
Online activity |
Recommended bandwidth* |
| Streaming music | 2 Mbps |
| Browsing the web, email, social media, shopping | 3 Mbps |
SD video streaming |
3 Mbps |
HD video streaming |
5 Mbps |
| HD video chatting | 10 Mbps |
| File downloads | 10 - 50 Mbps |
4K video streaming |
15 Mbps |
| HD online gaming | 25 Mbps |
Remote work/learning |
50 Mbps |
| 4K online gaming | 100 Mbps |
Large file downloads (e.g. game files) |
100 - 150 Mbps** |
* Indicates minimum recommended bandwidth required for each device to perform this activity. Each device activity takes away from total available bandwidth.
** Higher bandwidth is recommended for very large files to reduce download times. For instance, some games can be 60 GB or more.
Multiple factors will determine if you have adequate speed. You should consider how you use the internet, the size of your household, and which activities happen at the same time.
The internet speed test first finds the network server closest to you — you'll see the server name in the lower righthand corner of the testing window. Then, a "packet" of information is sent from your device to the network server and back. The amount of time it takes for that information to make the trip is your ping. Next, the test measures how fast a packet of data can be transferred from the network to your device (download speed) and back (upload speed).
Since the test is specific to the device you're using, a few factors can make a big impact on the result. Speed to your device will vary a lot based on using a wired or wireless connection. Over WiFi, speed is affected by the distance from the router or other WiFi access point, as well as any obstructions or signal interference. The age of your device can also make a huge difference in your speeds.
To get the best idea of your overall network speed (speed to your home), try testing over a wired (Ethernet) connection from a computer or laptop straight to the modem.
Ping, also called latency, is the amount of time it takes for your network to transfer information from your computer to a remote server and back. There will always be some latency over your network, but the lower this number, the better your performance. Online gamers especially keep an eye on ping, as high latency can lead to a noticeable delay between your actions and the actions of other players.
In talking about the speed you get and the speed you're paying for, it's important to understand the difference between speed to your building and speed to your device.
The first of these is the speed to your home or building, which tends to be pretty stable over time. Sign in to My CenturyLink to view your current plan details.
The best way to see the speed to your home (to the modem) is:
- Disconnect as many other connected devices as possible
- Run the speed test on a computer plugged into your modem with an Ethernet cord.
If you do both of these, the results should be very close to your plan speed. If you test in this way and it comes back significantly lower than your plan speed, you can run the Troubleshooter tool to look for problems on your line, or contact technical support for more help.
You ran your speed test, so what's next? We'll look at what those results tell you about your internet performance. Check out the top questions about speed test results, or watch the video below. Still curious? Scroll down to find more speed questions and answers.
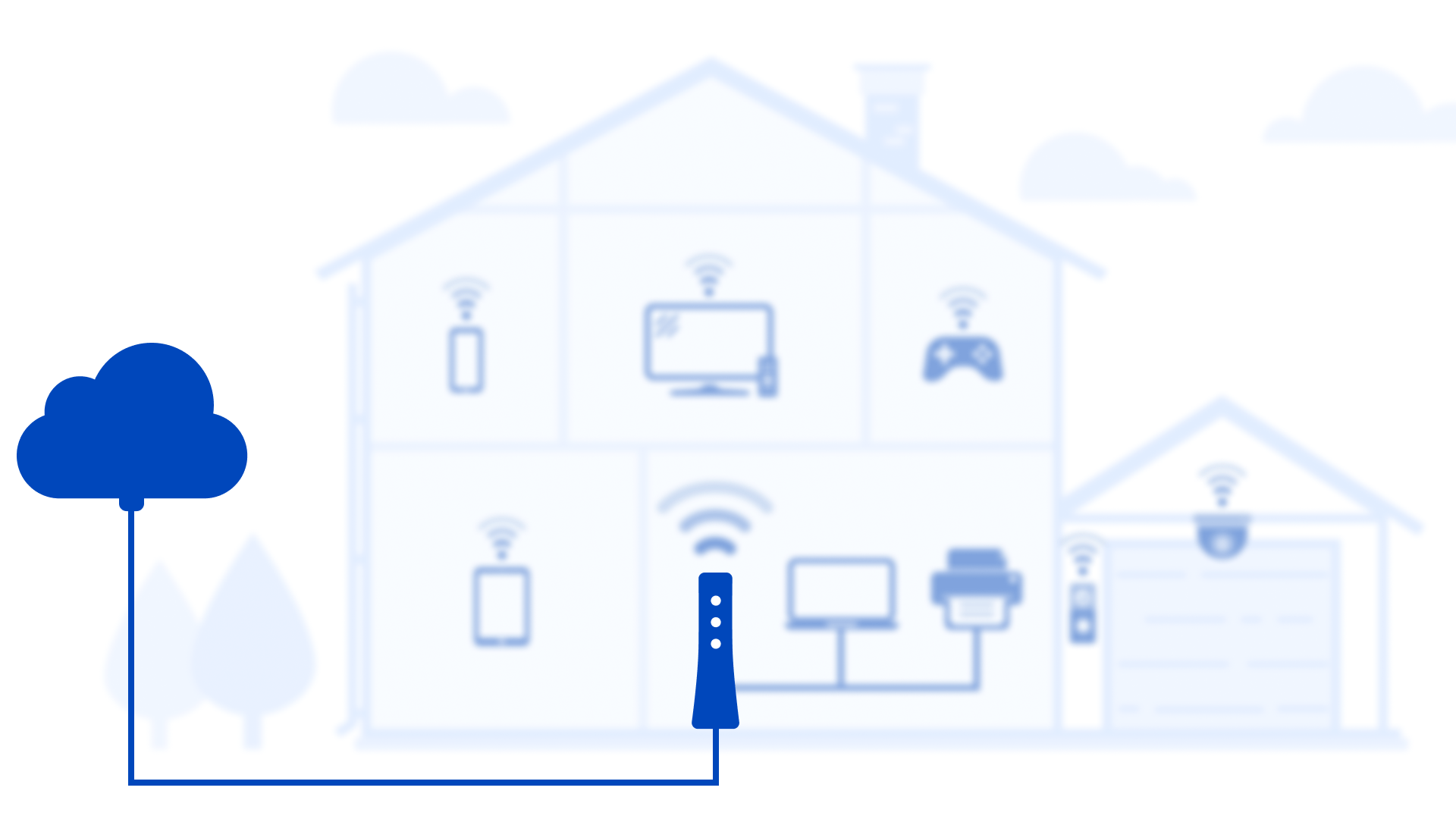
The outside network is the provider connection to your gateway/modem
Now, speed to your device is what our speed test measures and is much more variable due to changing factors. If you run the test on a WiFi-connected device, with several other devices in your home sharing your bandwidth, the result will be lower than your network speed (and your plan speed). This is because as more bandwidth is used across all connected devices, speed is reduced. Some speed is always lost over WiFi as well.
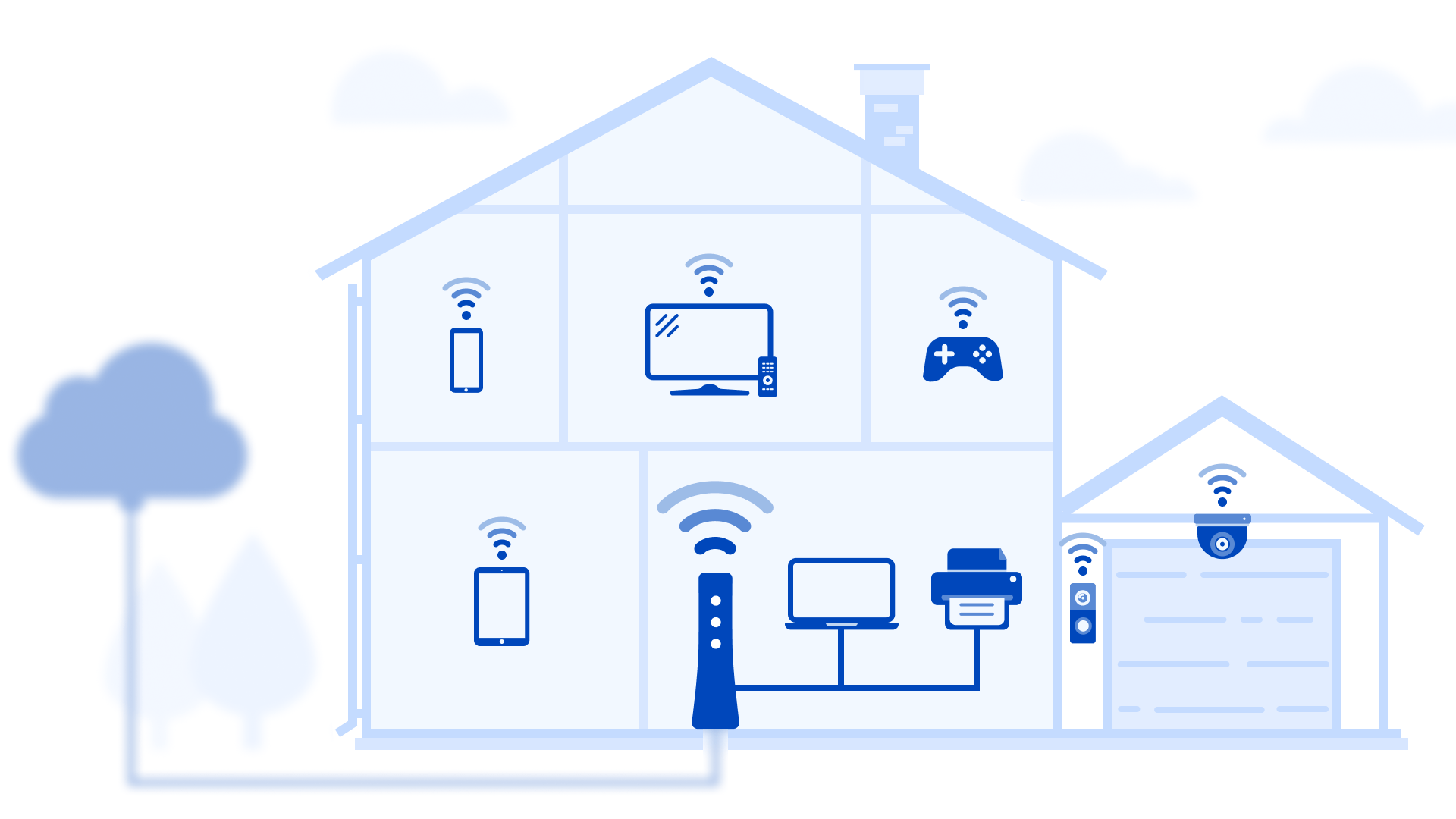
The inside network is the connection from your gateway/modem to all devices in your home
The internet speed test is based on real-time network conditions, which can change rapidly. As a result, tests taken within a few minutes of one another tend to vary, at least a little. Tests taken farther apart may differ even more, due to shifting network congestion and bandwidth availability. CenturyLink recommends running the test a few times at different points throughout the day to get a better understanding of fluctuations that occur at certain hours.
Download speed (Mbps or Gbps)
How fast data is transferred from the network to your device.
Upload speed (Mbps or Gbps)
How fast data is transferred from your device to the network.
More questions about internet speed
Based on your current internet speed plan and the information above, you may decide you need more bandwidth to meet your needs. So what are some options to increase your speed?
Upgrade to a higher speed: The simplest way is to upgrade to a faster plan. To see what speed options are available in your area, sign in to your account on My CenturyLink or the app, an
Add a second internet line: Another popular option is to add a second internet line, which instantly doubles your current speed. The additional line can be dedicated to remote work, gaming, or streaming needs. This is a good solution if you need more bandwidth but there are no higher speed plans available where you live.d check the My Products section.
You can check your current plan by signing in to your account on My CenturyLink or in the app.
- In the app, tap Services to see your current service speed.
- On My CenturyLink, scroll down on the home screen and look for the Internet Plan section. Or, select the Services tab at the top to see which details about your internet service.
Remember that your plan speed reflects the total bandwidth to your modem.
While bandwidth and speed aren't the same thing, they're closely related, which is why many people use the two terms interchangeably. The higher the bandwidth of service, the faster your connection speed will be on your devices. Both are measured in Megabits per second, or Mbps.
With high bandwidth, you can do more online activities at the same time, such as downloading music, browsing the internet, and streaming video in HD. A low-bandwidth connection, on the other hand, may lead to longer download and upload times, lower video quality, and buffering while streaming video or audio.
In DSL internet plans, the download speed tends to be much higher than the upload speed, because most users download more data than they upload. That trend is changing with fiber internet, which often offers a "symmetrical" connection, meaning the downstream and upstream bandwidth are equal. This can make some online activities much smoother, like online gaming and videostreaming. That's because these activities require more intensive data transfer in both directions (downstream and upstream) at the same time.
The internet speed test includes both upload and download speeds, so you don't have to test upload speed separately. The test results give you a full picture of your internet connection. Upload speed impacts how quickly you can send data from your devices through your network to another device or site on the internet. This is relevant when uploading files, gaming, live streaming your own videos, and video conferencing.
At this time, there is no remote option for the internet speed test. This means the device you're using for the test must be connected to the network you would like to test.
If you need to contact a tech support agent on the phone or chat for troubleshooting help, the agent can perform a remote speed test from our network to your modem, to help determine if you have internet connection issues.
Megabits per second (Mbps) is a measure of how fast data is transferred, so it's used to talk about bandwidth and speed. You will see this when you run our speed test, or when talking about the bandwidth of your internet service plan.
Megabyte (MB) is a measure of size, and is used to describe file size and storage capacity. Video files and high-resolution image files often have file sizes in MB. A megabyte (MB) is larger than a kilobyte (KB) and smaller than a gigabyte (GB).
Top Internet Topics
-
Check for an outage -
Troubleshooting slow internet -
Speed hub -
Upgrade your service -
WiFi support -
Internet security
View all Internet topics
CenturyLink Broadband Internet Service
Shop Accessories
Expand your CenturyLink internet service with top accessories from our partners, including WiFi performance, smart-home, streaming TV and more.
Was this information helpful?
Support topics