How to improve your WiFi signal
Whether you're setting up your WiFi network for the first time, or troubleshooting connection problems, these tips will help you maximize your wireless signal and improve slow or spotty WiFi.
Tips for optimizing your WiFi signal
If you’re working from home, are a die-hard gamer, or simply have a busy household, a strong and stable WiFi connection is important to keep all your devices up and running. There are a few things you can do to maximize your signal strength:
3. Find the best spot for the modem/router
4. Connect to the 5 GHz frequency
You can read the tips below or watch this video about boosting WiFi.
Tip #1: Find an optimal spot for your router
1. Check your wiring
It's worth taking a few minutes to make sure your general wiring, plugs, and cords are in good shape.
Check all cords and cables closely. Children, pets, and furniture can cause wires to be crimped or cut. If you do discover any damaged wiring, learn how to get it fixed.
Look and make sure both ends of all cords are firmly plugged in. Sometimes an issue is caused by a loose wire.
- The power cord is plugged in to a wall outlet and into the power port on the back of the modem.
- The DSL cord (often green) is plugged in to a working phone jack and into the green DSL port on the back of the modem. Both ends should click to indicate they're fully plugged in.
- If using a wired connection: The Ethernet cord (often yellow) is plugged in to an Ethernet port on a computer and in to an Ethernet ports on the back of the modem. If your modem has multiple ports, as shown in the image, try a different Ethernet port.

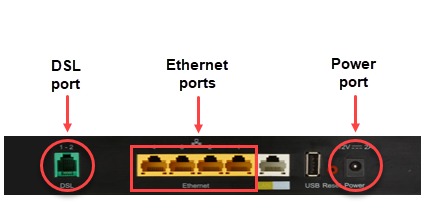
DSL and power ports on the back of the C4000LG
DSL and power ports on the back of the C3000A
(Other modems may look a bit different, but the ports will be similar.)
If you have both internet and home phone service from CenturyLink, then you will need DSL filters on all landline phones in the household. This ensures that your internet signal doesn't interfere with your landline.
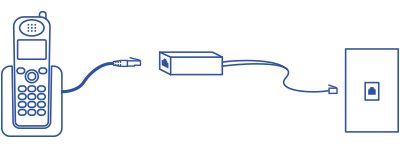
Plug the phone cord into a filter and then into the wall jack
Note: If you have cordless phones, you only need to install a filter on the phone base that plugs in to the wall jack; no filters are needed on the cordless units that only plug into an electrical outlet.
Make sure you do not have a filter installed between the modem and the wall jack.
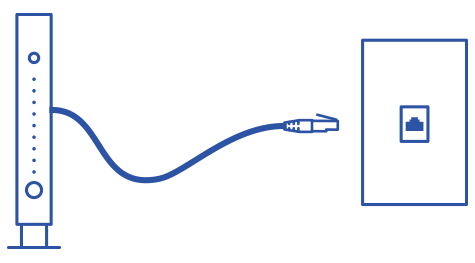
The DSL cord from the modem to the jack should not have a filter
If you want to plug both your modem and your phone into the same wall jack, you can use a DSL splitter, as shown in the diagram below.
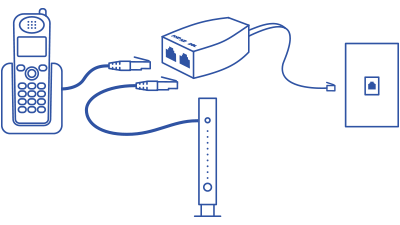
Or, use a DSL splitter to plug a phone and a modem into one wall jack
If you're a "do it yourself" kind of person, you can check to see whether there's a problem with the network signal by testing your line at the network box (NID). In most cases this can also be accomplished by signing in to your modem settings and checking your connection status.
2. Check your devices
Modems periodically get bogged down, and all digital devices can perform more poorly over time if not maintained and kept updated.
Modem fixes
- Reboot your modem manually or using the My CenturyLink app.
- Check the WiFi light on your modem to make sure it's working correctly.
- Make sure your modem is updated with the latest firmware version.
Device fixes
- Restart your device. This can fix many problems with software, memory and a slow connection.
- Shut down other apps or programs and browser tabs while streaming video or doing other high-bandwidth activities. This will free up memory and processor power on your device.
- Scan your computer with updated antivirus or security software. Malware such as a virus, trojan horse or worm can cause problems with your browser or your internet connection.
- Make sure your web browser (such as Firefox, Chrome, Safari, etc.) and all browser plug-ins are updated. You can use a third party website to help you do a browser check. Clearing browser cache may also help. You can search your browser's settings to "delete cookies" or "clear browsing history."
3. Find the best spot for your modem
One of the easiest ways to get the best WiFi signal throughout your space is to find a good spot for your router. Consider these tips for the best location:
- Central and closest to where the most devices will be using WiFi.
- A higher spot, like a shelf, ledge, or top of a bookcase.
- Nothing blocking the path between your router and your devices, such as heavy walls, thick windows, fish tanks, or large appliances (especially refrigerators).
- Away from heat sources.
Click below to see illustrations for more detailed tips and explanations.
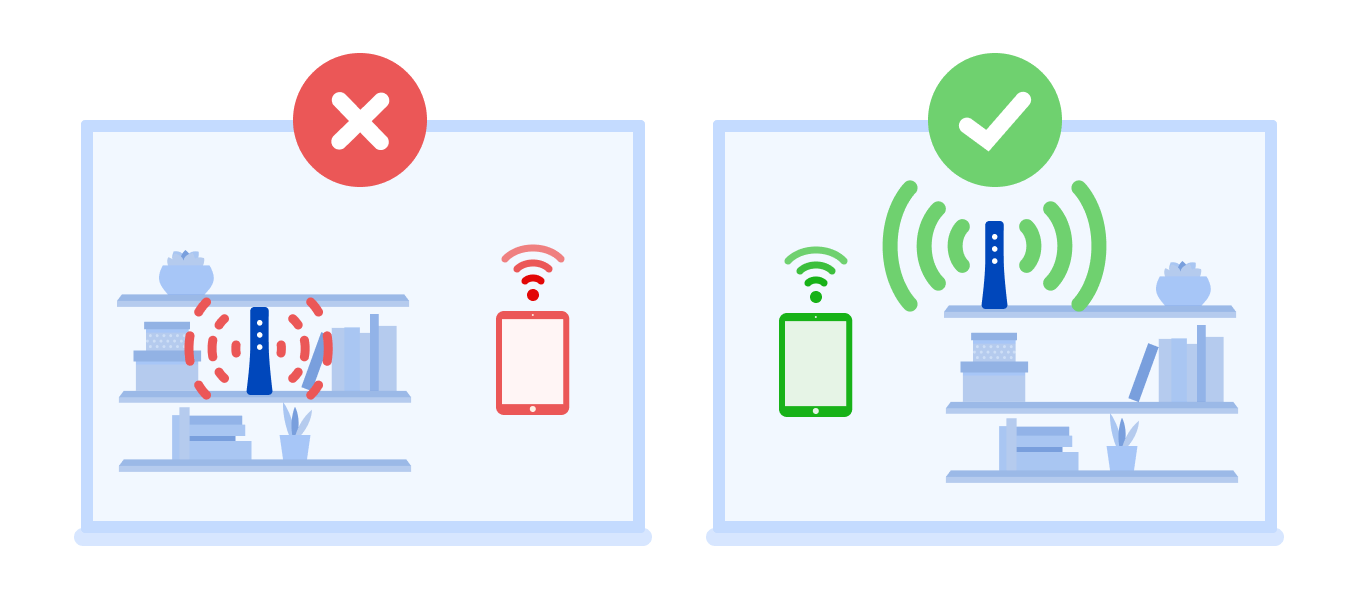
Place your router out in the open for better connection strength. Avoid closets and crowded bookshelves.
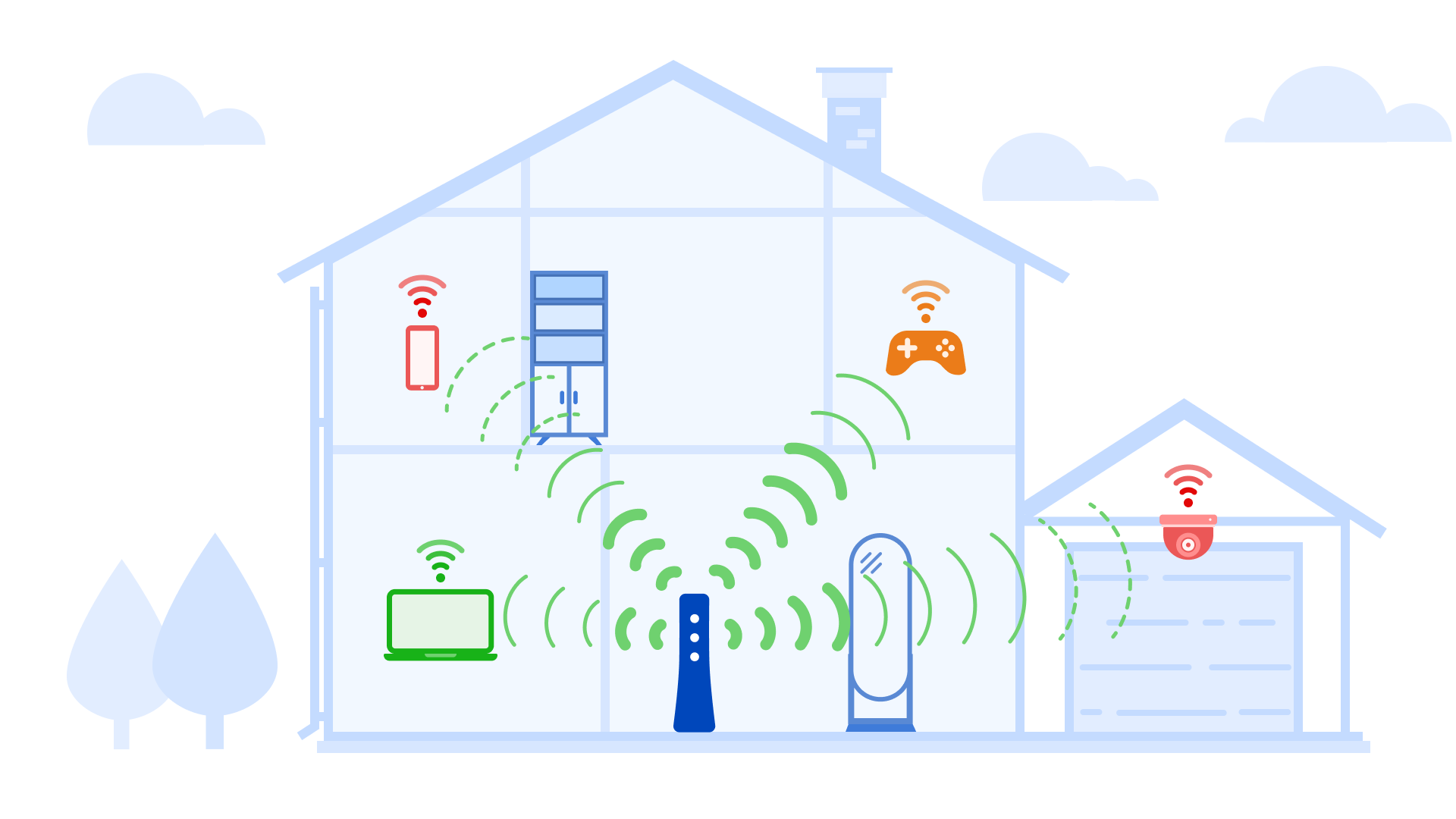
Distance, as well as obstructions like walls and floors, can weaken your WiFi signal strength.
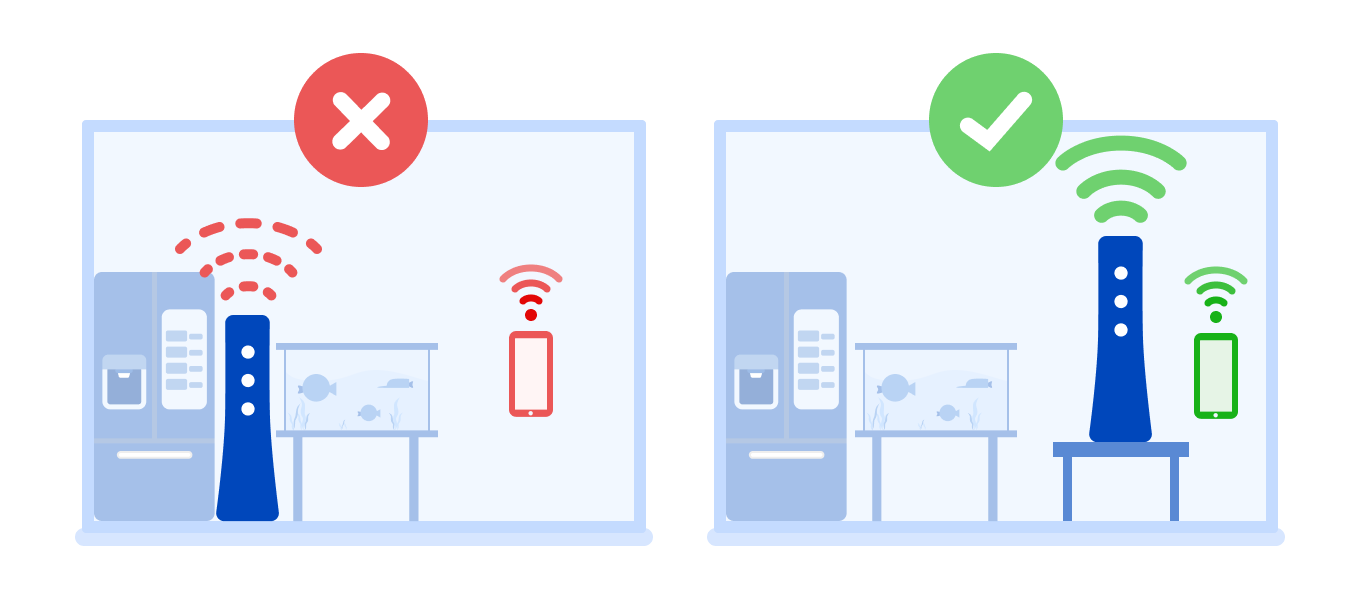
Avoid placing your router close to heavy, dense appliances and large metal or glass objects.
| Barrier | WiFi loss (in decibels) |
|---|---|
| Drywall / Hollow wood door |
3-4 dB |
| Brick wall |
6 dB |
| Concrete wall or floor |
8 dB |
| Refrigerator |
19 dB |
4. Use the 5 GHz frequency
If you have a newer modem, opt for the 5 GHz frequency signal to get a stronger connection and avoid interference from surrounding devices.
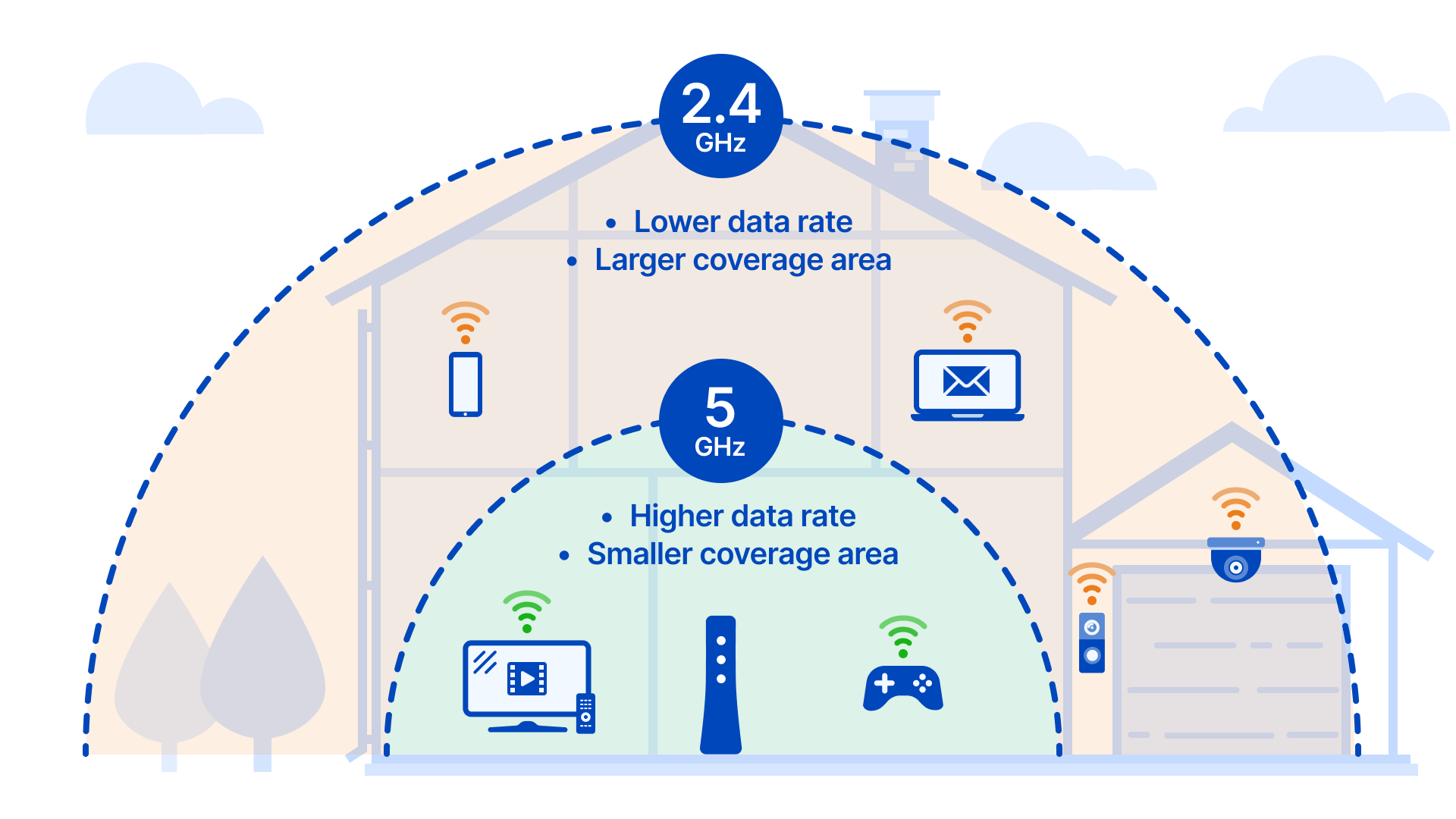
Here's why: Devices that use the same 2.4 GHz frequency range can hurt your internet speed. These include many microwaves, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, TVs, wireless security systems, baby monitors, garage door openers, and more. Some of these create interference even when the device is off. Many newer routers will automatically switch devices to a faster frequency, but if your router is more than a couple of years old, you may need to manually change to a 5 GHz connection to get the faster frequency. Read more about the difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, and find out how to change the wireless channel on your router to minimize congestion.
Put at least 5-10 feet of space between other devices and your router to help reduce interference and competition.
5. Free up bandwidth
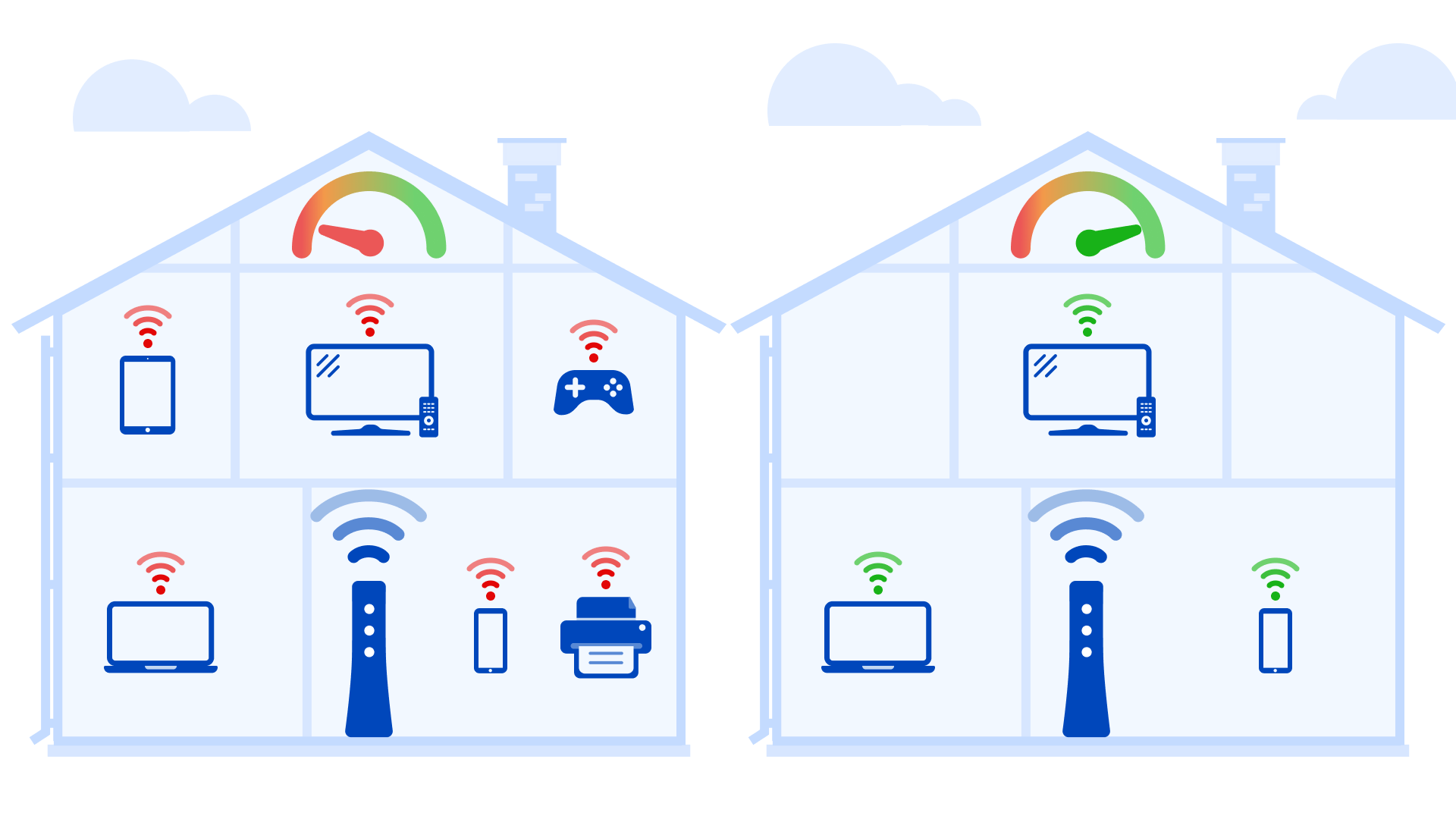
Limit the number of devices in your home that share your WiFi network during peak usage hours. The more bandwidth is used in total, the lower the speed you see on each device. Power off or disconnect devices that you aren't actively using. If you have slow internet speed, try making a household schedule to manage which devices can be used at different times.

As you connect more devices to your WiFi, the signal strength and connection speed will go down.
Here's why: The number of devices running at the same time impacts your internet speed significantly, because they all divide up your available bandwidth. The more devices you add to the network, the less speed you'll get on each device. Gaming systems, video streaming devices, and a number of smart home appliances can eat up a lot of bandwidth. Plus, many connected devices are always on and run updates in the background, which can further slow speeds down.
Video: 5 tips to boost WiFi
All about WiFi
Top Internet Topics
-
Check for an outage -
Troubleshooting slow internet -
Speed hub -
Upgrade your service -
WiFi support -
Internet security
View all Internet topics
Top Tools
Was this information helpful?
Support topics






.png)